Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome
Image MDPI
"Breaking Down PCOS: Understanding a Complex Hormonal Disorder"
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a common hormonal disorder that affects women of reproductive age. It is a complex condition that is caused by an imbalance of hormones in the body, and it can lead to a range of symptoms, including irregular periods, weight gain, and acne. In this blog, we will explore what PCOS is, its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options.
What is Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)?
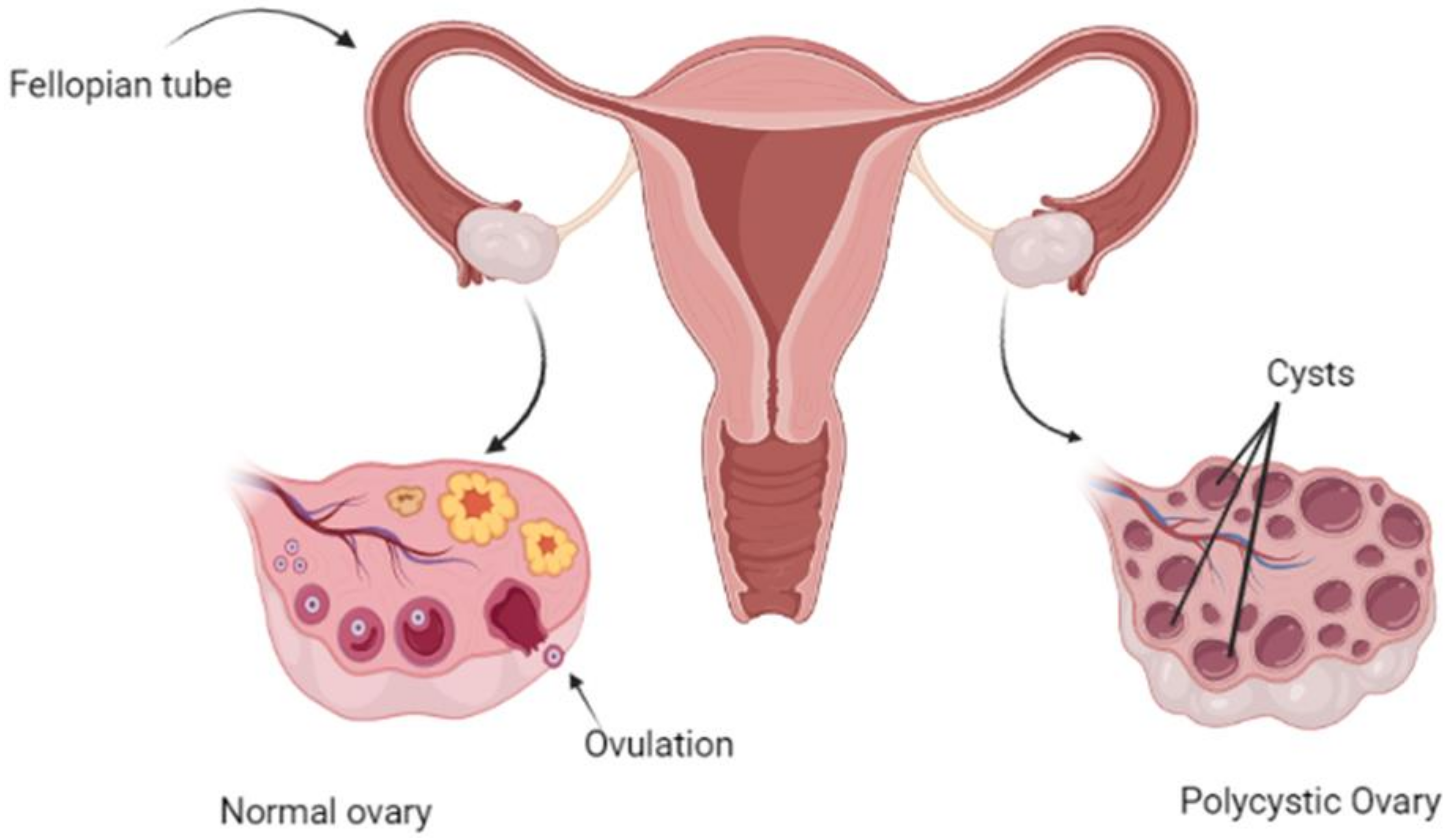
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a hormonal disorder that affects the ovaries, which are the reproductive organs responsible for producing eggs. PCOS is characterized by the presence of small, fluid-filled sacs or cysts on the ovaries, which can lead to hormonal imbalances in the body. These imbalances can cause a range of symptoms, including irregular periods, acne, weight gain, and infertility.
What are the Causes of PCOS?
The exact cause of PCOS is not yet known, but it is believed to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Women with PCOS tend to have higher levels of androgens (male hormones) in their bodies, which can cause the ovaries to produce more follicles than usual. This can lead to the formation of cysts on the ovaries.
In addition to genetics, other factors that can contribute to the development of PCOS include insulin resistance, inflammation, and obesity. Insulin resistance occurs when the body becomes less sensitive to insulin, which is a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels. This can lead to an increase in insulin production, which can cause the ovaries to produce more androgens.
Symptoms of PCOS
The symptoms of PCOS can vary from person to person, but some of the most common symptoms include:
1. Irregular periods - Women with PCOS may have irregular periods or may not have periods at all.
2. Acne - High levels of androgens in the body can cause acne and other skin problems.
3. Weight gain - Women with PCOS may have difficulty losing weight or may gain weight easily.
4. Excess hair growth - High levels of androgens in the body can cause excess hair growth on the face, chest, and other areas of the body.
5. Infertility - PCOS can make it difficult for women to conceive.
Diagnosis of PCOS
Diagnosing PCOS can be challenging, as there is no single test that can confirm the condition. Your doctor may start by asking about your medical history and performing a physical exam. They may also order blood tests to check your hormone levels, as well as an ultrasound to check for the presence of cysts on your ovaries.
Treatment options for PCOS
There is currently no cure for PCOS, but there are several treatment options available that can help manage the symptoms of the condition. Some of the most common treatment options include:
1. Lifestyle changes - Making changes to your diet and exercise routine can help improve insulin resistance and manage weight gain.
2. Medications - Your doctor may prescribe medications to help regulate your menstrual cycle, reduce androgen levels, or improve insulin sensitivity.
3. Surgery - In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove cysts on the ovaries or to restore ovulation.
Conclusion
If you think you may have PCOS, it's important to talk to your healthcare provider. With proper diagnosis and treatment, most women with PCOS are able to manage their symptoms and maintain good health.
PCOS is a chronic condition that requires ongoing management. Treatment options can help to manage symptoms and improve fertility outcomes for women who are trying to conceive. Women with PCOS should work closely with their healthcare provider to develop a treatment plan that is tailored to their individual needs.